Capital and Corporal Punishment in AngloSaxon England

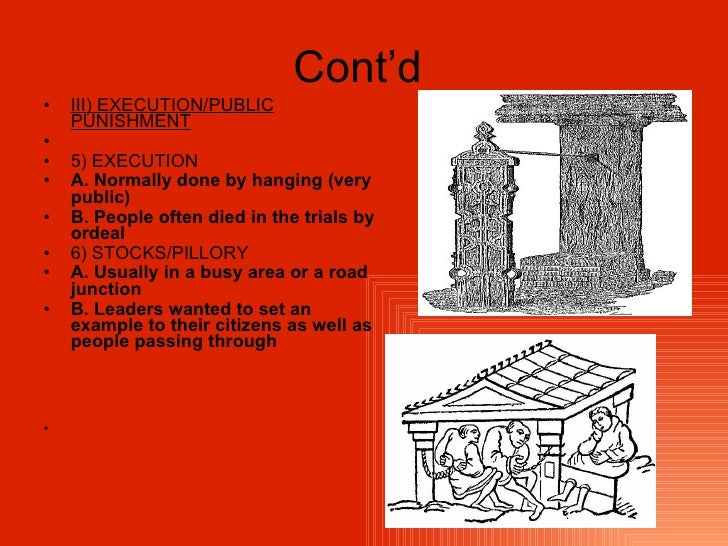
In Anglo-Saxon England they believed in a policy of retribution, for example a minor crime such as being drunk and disorderly would receive a punishment such as the stocks and the pillory.These were used to publicly humiliate the criminal, the public may have even thrown rubbish or verbally abused them.For crimes such as assault the criminal may be subjected to corporal punishment such as.
Crime and Punishment in AngloSaxon times BBC Bitesize
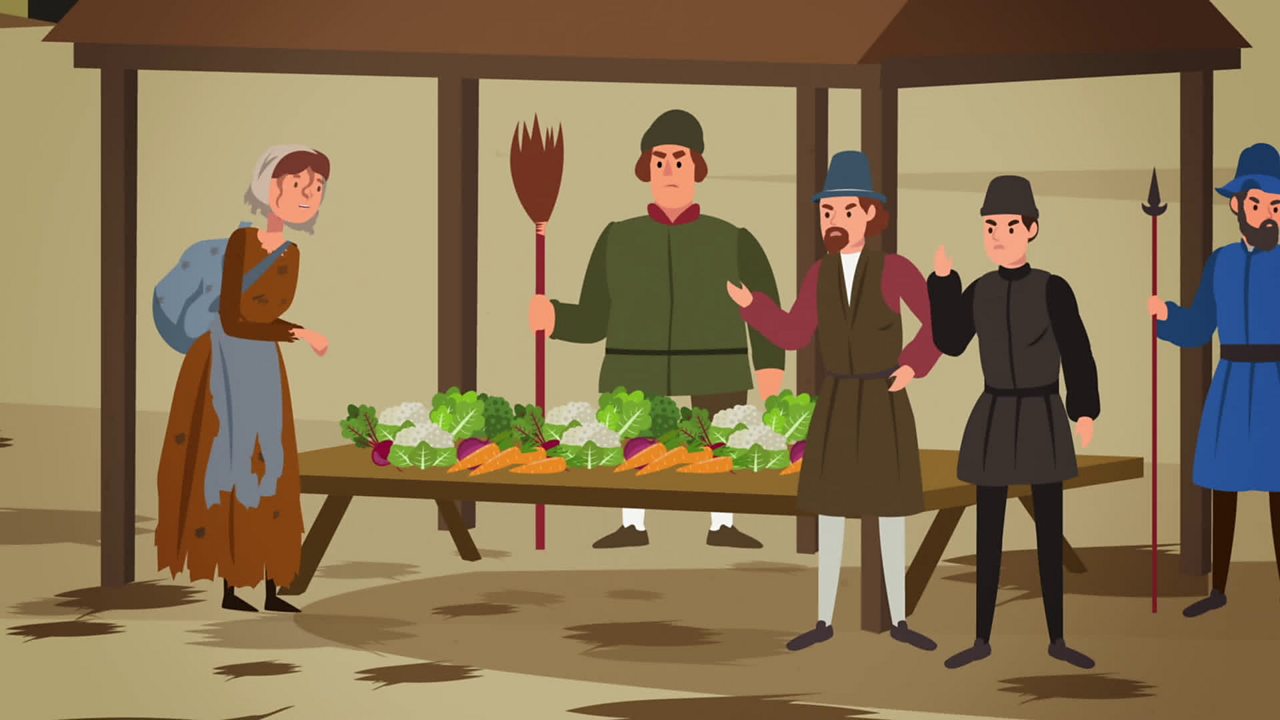

This video covers Anglo Saxon laws, crimes and punishments: It explains what a gemot and a witan are, and also the dooms and a Hundred Court together with s.
Crime and Punishment GCSE, c1000 c1500 Anglo Saxon Law Enforcement YouTube

5 Incarceration as Judicial Punishment in Anglo-Saxon England; 6 Earthly Justice and Spiritual Consequences: Judging and Punishing in the Old English Consolation of Philosophy; 7 Osteological Evidence of Corporal and Capital Punishment in Later Anglo-Saxon England; 8 Mutilation and Spectacle in Anglo-Saxon Legislation
AngloSaxons were not all equals Crime and Punishment Year 5 Pango

As we have observed, the majority of atonements comprised monetary fines, but for a range of offences from the reign of Ine onwards, courts could impose the death penalty, of which more shortly. Non‐capital punishments found in the late Anglo‐Saxon laws include exile, forfeiture of land, and mutilation.
EDEXCEL GCSE History Crime and Punishment AngloSaxons YouTube
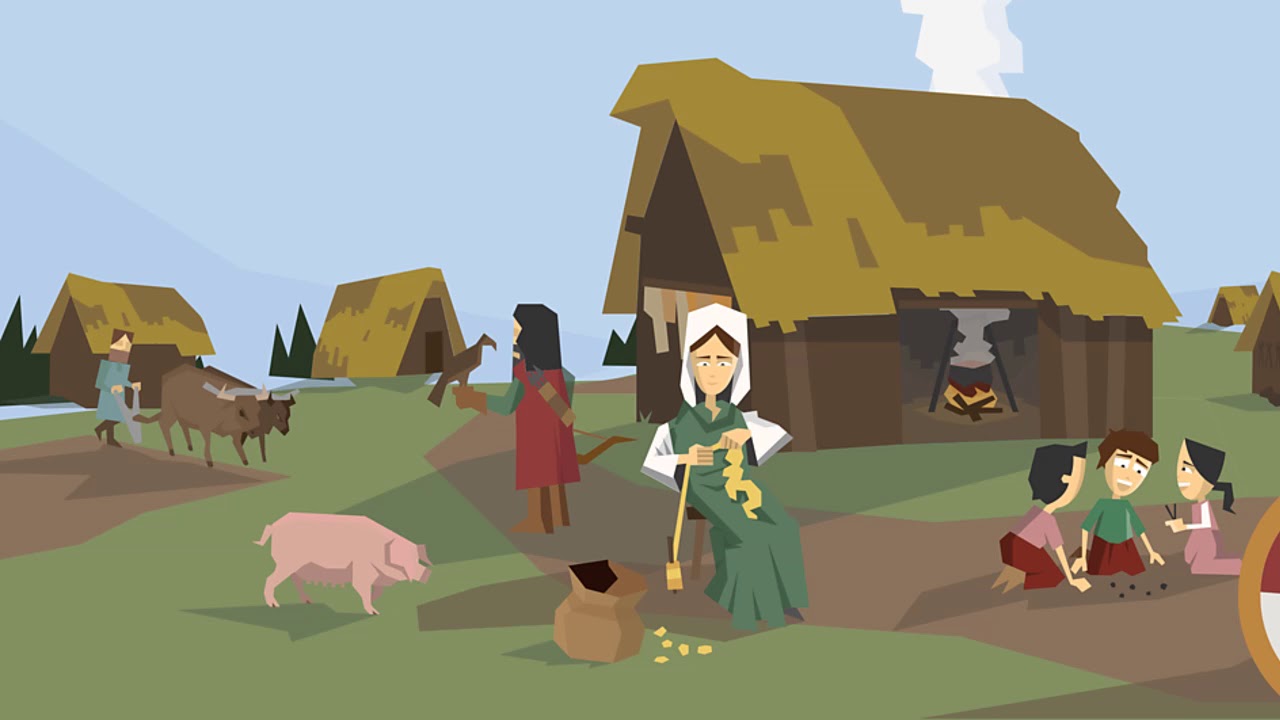

GCSE; Edexcel; Crime and punishment in medieval England, c.1000-c.1500 - Edexcel New crimes in Norman England. Justice in Anglo-Saxon England was the responsibility of the local community, with.
Edexcel GCSE 91 Crime & Punishment L3 How did Anglo Saxons catch and try criminals? Teaching

Part of History Crime and punishment in Britain, c.1000 to the present day After he became king of England in 1066, William I continued many Anglo-Saxon methods of law enforcement and also added.
Why the trial by ordeal was actually an effective test of guilt Aeon Ideas

The ten essays in this volume engage legal, literary, historical, and archaeological evidence to investigate the role of punishment in Anglo-Saxon society. CONTENTS 1 Introduction: Capital and Corporal Punishment in Anglo-Saxon England. Nicole Marafioti and Jay Paul Gates 2 When Compensation Costs an Arm and a Leg Valerie Allen 3 Beginnings and.
Crime and Punishment — AngloSaxons and Vikings (Years 56) CGP Plus

Crime and punishment in medieval England, c.1000-c.1500 - Edexcel Crimes and law making in Anglo-Saxon England Justice in Anglo-Saxon England was the responsibility of the local community, with.
Anglo Saxons Crime and Punishment Information PDF Anglo Saxons Justice

Crime and Punishment in Anglo-Saxon England Elements in England in the Early Medieval World DOI: 10.1017/9781108943109 First published online: August 2020 Andrew Rabin University of Louisville Author for correspondence: Andrew Rabin, andrew.rabin@louisville.edu Abstract:
crimeandpunishmentinanglosaxonengland PDF Anglo Saxons Crimes

The church had its own courts and a different system of punishment. The Anglo-Saxons didn't have prisons. Most people found guilty of crimes were punished with fines. Some crimes, such as treason.
Understanding Crime and Punishment in Medieval England PDF Trials Anglo Saxons

Crime and Punishment - the Anglo-Saxons Fact Sheet could be Fail: Trial by ordeal If there were not enough witnesses or evidence to find a person guilty the court could order a trial by ordeal: if the accused passed the test they were evidently protected by God and therefore innocent. If he failed he was guilty and would be executed. Trial by.
10001066 Crime in AngloSaxon England Crime & Punishment GCSE History Revision YouTube

How did the Norman invasion change attitudes to crime and punishment during medieval times ? The following sources and connected activities will help you understand how law and order was maintained under the Anglo-Saxons, how fair was the Anglo-Saxon and Norman justice system and what changes were made after the Norman onquest in ò ò.
AngloSaxon Laws
Crime and Punishment in Anglo-Saxon England. $22.00 ( ) USD.. and, in many cases, challenged. And perhaps most importantly, they provide unparalleled insight into the experiences of Anglo-Saxon England's diverse inhabitants, both those who enforced the law and those subject to it.. Anglo-Saxon to Anglo-Norman England. Lives of Edward the.
Crime And Punishment In Anglo Saxon England

GCSE; Edexcel; Crime and punishment in medieval England, c.1000-c.1500 - Edexcel Law enforcement and punishment in Anglo-Saxon England. Justice in Anglo-Saxon England was the responsibility of the.
AngloSaxon crime and punishment revision questions History KS4 Teachit

Part of History Crime and punishment in Britain, c.1000 to the present day Most punishments used in Anglo-Saxon and Norman England continued throughout medieval England. In the 12th century, Henry.
Crime And Punishment In Anglo Saxon England
It's the year 1000 and England's population is thought to be somewhere between 1.7 and 2 million. About 90% of people live in the countryside. These people i.